Firesearch.dev - Serverless full-text search
Deployment guide
This guide walks you through deploying Firesearch to Google Cloud Platform.

Did you know? You can run Firesearch on your dev machine using the Firestore emulator and Docker. Follow our tutorial to get started.
Putting Firesearch into production
Firesearch is a middleware service that sits between Firestore and your backend services, and your public web and mobile clients.
Step 1. Enable Google Cloud APIs
Firesearch uses a number of Google Cloud APIs and services.
You should ensure the following are enabled in your Google Cloud project:
- Cloud Run to host the Firesearch instances
- Google Cloud Firestore (in Native mode) to store index data and Firesearch metadata
- Google Cloud Console > Security > Secret Manager for providing secret strings
- Google Cloud Console > Operations > Error Reporting and Google Cloud Console > Operations > Logging for troubleshooting and maintenance
Billing may be required in GCP for some of these services to work—you will be prompted by the Google Cloud Console UI as you enable the services.
Now that you have enabled all the appropriate APIs, you can set up the secrets for Firesearch.
Step 2. Add required secrets
Firesearch uses the Google Cloud Console > Security > Secret Manager to get the required secret strings.
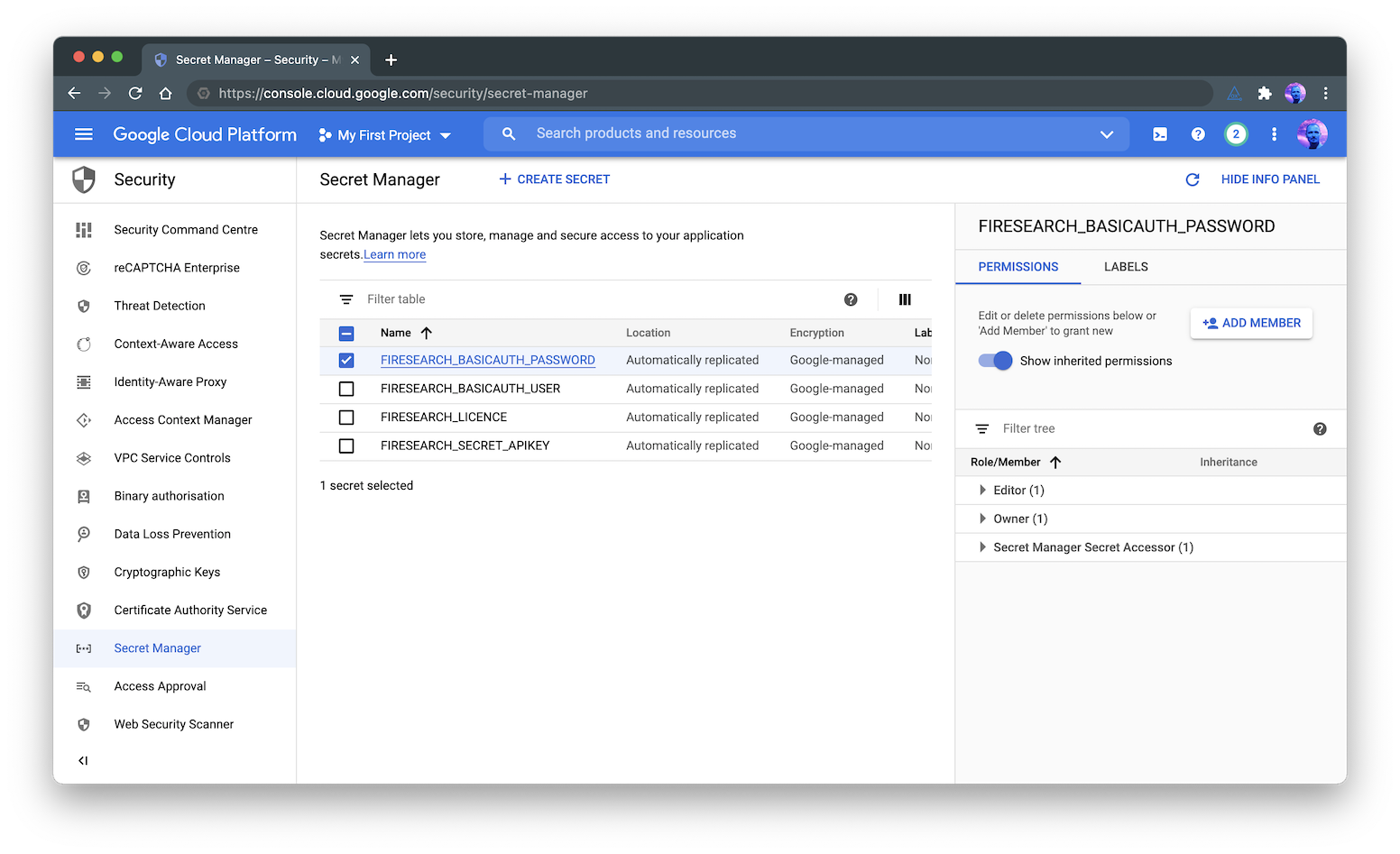
Use the Secret Manager user interface in the Google Cloud Console to add the four secrets listed below.
Secret permissions
For each secret, you must give the Secret Manager Secret Accessor permission role to the service account you will be using to run the instance.
You can use the default service account (just start typing gserviceaccount to see the account in the dropdown). Secrets
You should add all four of the following secret strings:
-
FIRESEARCH_API_KEY- (string) A key string that must be sent in theX-API-Keyheader—can be shared with trusted clients (i.e. backend services or cloud functions) -
FIRESEARCH_BASICAUTH_USER- (string) The "Basic" authentication username to access the Firesearch Console -
FIRESEARCH_BASICAUTH_PASSWORD- (string) The "Basic" authentication password to access the Firesearch Console -
FIRESEARCH_LICENCE- (string) This is the licence key you get from https://firesearch.dev/licences
Once you have added these secrets and verified the permissions, you are ready to create the Firesearch instance.
Step 3. Create service on Cloud Run
In this section you will get the Firesearch service running in production on Google Cloud.
- Open the Cloud Run console
- Click the CREATE SERVICE button
- In Service settings, configure the Deployment platform or use the defaults if you're not sure
- Enter a service name, for example
firesearch - Click NEXT to access Configure the service's first revision
- Enter the Firesearch Container image URL:
- Expand the Advanced settings and select the CONTAINER tab
- For Service account select the Default compute service account (or any account that has the appropriate permission to read the secrets)
- Under Capacity, allocate
256 MiBmemory (or512 MiBif you're using an ML image) - Select the VARIABLES tab
- Click ADD VARIABLE and add your Google Cloud Project ID:
- Name:
PROJECT_ID - This value must match the assigned project in the licence—Manage your licences on Firesearch.dev
- This value must also match the project in which you are using Cloud Run
- Name:
- Click NEXT to continue
- In the Configure how this service is triggered section, you have two choices:
- If you intend to interact with Firesearch externally (in a browser or on mobile) choose Allow unauthenticated invocations (Firesearch security still applies)
- For backend only access, you can use the Require authentication option
- To learn more about the implications of this decision, see our Security guide
- Review your settings and click CREATE
Check the logs
If Firesearch fails to start, you will find useful information in the logs:
Step 4. Test your deployment
Once the instance is running, access the instance URL (provided by Cloud Run) in a browser.
Once Firesearch is running, you will be prompted to enter the "Basic" authentication credentials that mirror those in your secrets.
Once authenticated, you will be able to access the Firesearch Console.
Firesearch is now running in your environment.
You did it!
Congratulations, you are successfully running Firesearch in production.
- You are free to do the Live tutorial, but remember that it will write real data to your production Google Cloud Firestore
- Firesearch API is running alongside the console (at
/api) so you can start to write code to interact with it using the Client libs and SDKs
Common problems
If Firesearch fails to start, you will find useful information in the logs:
If Firesearch starts but is unable to run, you will be presented with an error message in the browser when you access the console.
After you make changes, you will need to deploy the instance again which you can do using the EDIT AND DEPLOY NEW REVISION button, and then clicking DEPLOY.
Unable to connect to firestore
You may see an error similar to:
Unable to connect to firestore: rpc error: code = NotFound desc = The project does not exist or it does not contain an active Cloud Datastore or Cloud Firestore database.Firesearch is having trouble connecting to Firestore.
- Ensure you have API Firestore enabled (see instructions in the full error message—look for the setup link)
- Double-check the steps in Step 1. Enable Google Cloud APIs
Firesearch unable to start: FIRESEARCH_SECURITY=on: unable to get secret
Firesearch is unable to read the secrets from the Secret Manager.
Usually this is a permission problem. Ensure the service account you used to create your Cloud Run instance has at least the Secret Manager Secret Accessor role.